Foot and ankle
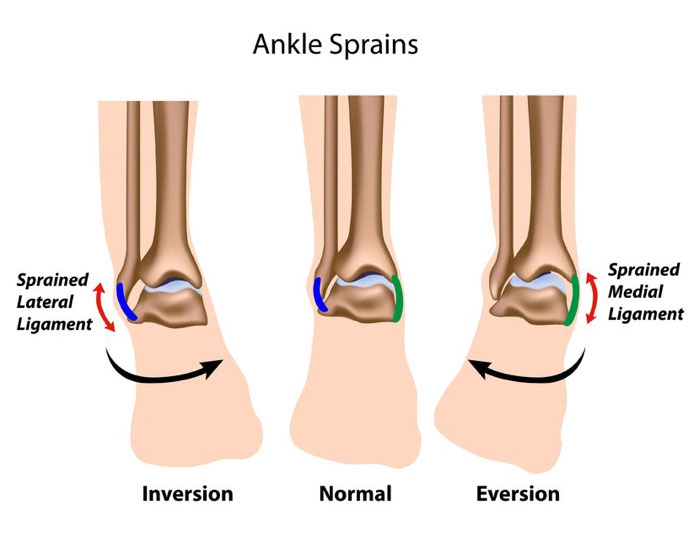
Foot and ankle is a complex structure responsible for taking on the full load of the body, stabilizing the lower limbs, active control of motions, constant biofeedback for balance, and impact absorption. The continuous load and motion of the structure make it more vulnerable to injuries.
Symptoms often experienced are pain locally to one or more of the joints in the ankle or sharp or dull aching pain in or around the joint. Associated symptoms are swelling, clicking, clunking, tingling, numbness and pins and needles.